Week 13 Geographic Distributed Development
http://www-128.ibm.com/developerworks/rational/rationaledge/admin/current.html
Assignment #1 Knowledge Sharing Weblog (10%) Tasks: Each student should keep a weekly weblog (blog) to document their learning experience and what they learned. The main purpose of the weblog is to encourage you to learn independently as well as a way to share what you learned with others in the class. Each student is required to give a short 5-minute talk on your blog in class.
http://www-128.ibm.com/developerworks/rational/rationaledge/admin/current.html
In fact, if all the software develop are developing with the RIP methodology, everything should be alright. The global software developer can get the advantage from it since the detail divide of the working force among the developers all around the world: under the XP, pair programming works as the American developer are sleeping, the
Open-source software, well, they are created by a group of volunteer developer around the world. Developers seldom bounded by these paper work. As the result, the quality of the software is extremely good but no one would use the MySQL to replace the Oracle. What’s the reason? Undoubtedly, Oracle provide a lot of “evidence” to show their products are really works and reliable but throwing several tones of paper and documents to show that, but not the MySQL.
In my point of view, RUP and XP are the tools to management a group of developers in the software vendors, not for the purpose to creating a good/extremely good software sadly.
http://www.objectmentor.com/resources/articles/RUPvsXP.pdf
Needs of the developer and customer
We have mentioned a lot what do the software engineers need to figure out what to do and what do not do under the Rational Unified Process, so we may think about what the NEEDS of the developer and the needs of the clients.
When comparing with the Extreme Programming, RUP provide more guidelines for a group of developer to build software in a disciplined, elegant and productive way in the limited time. Although XP is fast and fewer set of rules to follow, it is difficult to follow when developers are going to build a reliable and systematic, real-time, bug-free software.
In person, I would prefer XP since less documentations and rules means developers have more room to focus on the project coding, not in the planning stage. A workable software still better than a good written documentation but fairly acceptable software.
Week 6 – UML
What is UML?
UML stands for the Unified Modeling Language. UML is the OMG’s most used specification and the way the world models not only application structure, behavior and architecture, but also business process and data structure.
UML 1.5: the current official version
http://www.omg.org/technology/documents/modeling_spec_catalog.htm#UML
UML resource page
Borland UML tutorial
http://bdn.borland.com/article/0,1410,31863,00.html
The heart of object-oriented problem solving is the construction of a model. The model abstracts the essential details of the underlying problem from its usually complicated real world. That’s the reason why we would like to use the UML to model the real world while we are programming.
So, what is UML? UML stands for “Unified Modeling Language”. Why does the UML so important? Since writing software is something that does not like constructing a building. The more complicated the underlying system, the more critical the communication among everyone involved in creating and deploying the software. The UML is application to object-oriented proclaiming solving. Anyone interest in learning UML must be familiar with the underlying tent of object-oriented problem solving. How can we get started? We use model. What is mode? A model is an abstracting of the underlying problem. The domain is the actual world from which the problem comes.
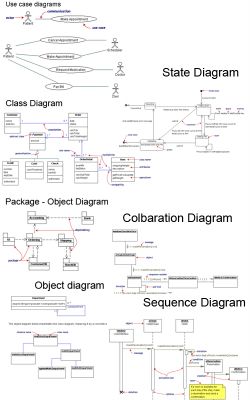
At the center of the UML are its nine kinds of modeling diagrams, which we describe here:
1. Use case diagrams
2. Class diagrams
3. Object diagrams
4. Sequence diagrams
5. Collaboration diagrams
6. Statechart diagrams
7. Activity diagrams
8. Component diagrams
9. Deployment diagrams
UML are quiet simple. With several simply rules, we can adopt to the complicated world with simply diagram. It is really a great innovation and hopefully the upcoming version UML 2.0 will be much more
Huge of modeling tools
Poseidon for UML
Borland Together
http://www.borland.com/together/
